Aluminum Fluoride: Navigating Environmental Challenges Through Versatile Applications in Wastewater and Air Treatment
Aluminum fluoride (AlF3), a versatile inorganic compound, has found significant application in the treatment of both wastewater and air pollutants. This article explores the application, reaction mechanisms, and industrial utilization of aluminum fluoride in addressing environmental challenges.
Mechanisms in Wastewater Treatment
1. Coagulation and Precipitation
Aluminum fluoride functions as a coagulant in wastewater treatment by promoting the agglomeration of suspended particles. Upon introduction into wastewater, it undergoes hydrolysis, leading to the formation of aluminum hydroxide flocs. These flocs entrap impurities and facilitate their settling, simplifying their removal during subsequent processes.
2. pH Adjustment
The ability of aluminum fluoride to adjust pH is pivotal in wastewater treatment. The addition of aluminum fluoride helps regulate the acidity or alkalinity of the wastewater, optimizing the conditions for coagulation and precipitation. Proper pH control enhances the efficiency of subsequent treatment steps.
Reaction Mechanism
The primary reaction involves the formation of aluminum hydroxide (Al(OH)3) through the hydrolysis of aluminum ions in the presence of water:
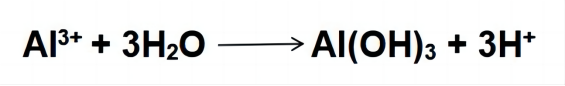
This aluminum hydroxide then reacts with fluoride ions:
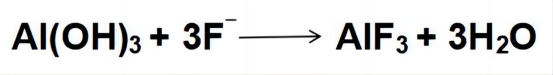
Aluminum Fluoride in Air Treatment
1. Adsorption of Gaseous Pollutants:
Aluminum fluoride serves as an efficient gas adsorbent in air treatment applications. Its surface properties allow for the adsorption of noxious gases, such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs), contributing to the reduction of atmospheric pollutants.
2. Reaction with Harmful Emissions:
In air treatment, aluminum fluoride reacts with specific pollutants, such as hydrogen fluoride. The chemical reaction results in the formation of stable compounds, effectively eliminating hazardous emissions from the air.
Industrial Applications
1. Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants
Municipal wastewater treatment plants incorporate aluminum fluoride to enhance the removal of suspended solids and improve the overall efficiency of water clarification processes. Its application ensures compliance with environmental standards before discharging treated water.
2. Industrial Effluent Treatment
Various industries, including manufacturing, petrochemicals, and metal processing, utilize aluminum fluoride to treat effluents. Its coagulation properties assist in the removal of pollutants, promoting responsible wastewater management.

3. Semiconductor Manufacturing
The semiconductor industry utilizes aluminum fluoride for its purity and effectiveness in water treatment. It plays a crucial role in removing impurities from water used in various semiconductor manufacturing stages, ensuring the production of high-quality products.
4. Air Pollution Control in Factories
Industries with emissions of volatile pollutants, such as the manufacturing sector, deploy aluminum fluoride to control air pollution. Its gas adsorption capabilities make it an effective tool in reducing the environmental impact of airborne pollutants.
In conclusion, the multifaceted applications of aluminum fluoride in wastewater and air treatment underscore its versatility and importance in contemporary environmental management practices. Its judicious use promises to contribute significantly to sustainable industrial processes and the mitigation of environmental pollution.
- Fluoride Salt
- Ammonium Fluoride
- Sodium Fluoride
- Potassium Fluoride
- Sodium Hydrogenfluoride
- Potassium Bifluoride
- Magnesium Fluoride
- Aluminium Fluoride
- Barium Fluoride
- Lithium Fluoride
- Strontium Fluoride
- Nickel Fluoride
- Zinc Fluoride




