Potassium Fluoroborate: A Catalyst for Excellence in Aluminum and Magnesium Refining
In the fascinating world of metal refining, potassium fluoroborate plays a pivotal role in enhancing the quality of aluminum and magnesium. This unassuming compound, with its unique properties, serves as a catalyst in the refinement process, contributing to the production of high-grade metals widely used in various industries.
Before delving into the specifics of potassium fluoroborate's role, let's grasp the fundamentals of aluminum and magnesium refining. Both metals are extracted from their respective ores through complex processes involving electrolysis and reduction reactions. The challenge lies in purifying them to meet stringent industrial standards.
The Magic of Potassium Fluoroborate:
Enter potassium fluoroborate, a chemical compound that acts as a refining agent during the production of aluminum and magnesium. This compound is adept at facilitating the removal of impurities, ensuring the final metal products boast superior quality and performance.

Selective Impurity Removal:
Potassium fluoroborate excels in its ability to selectively remove unwanted impurities, such as oxides and non-metallic inclusions, from the metal matrix. This is crucial because impurities can compromise the mechanical and chemical properties of aluminum and magnesium, affecting their usability in various applications.
Enhanced Electrolysis Efficiency:
In the aluminum refining process, potassium fluoroborate aids in optimizing the efficiency of electrolysis. By promoting smoother current flow and reducing resistance, this compound contributes to the overall efficacy of the refining process. The result? Purer aluminum ready for applications ranging from aerospace to packaging.
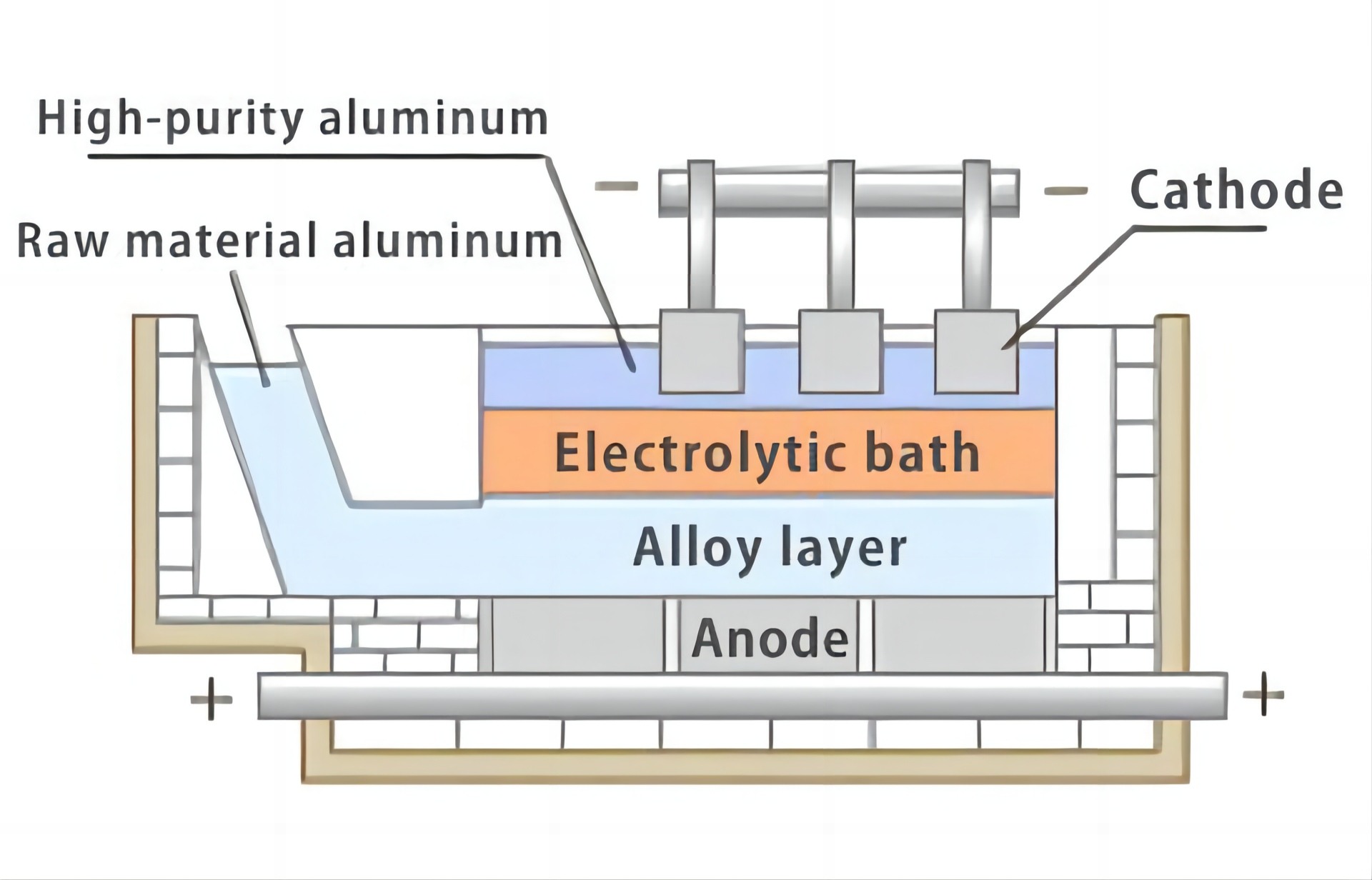
Magical Magnesium Refinement:
Similarly, in magnesium refining, potassium fluoroborate plays a vital role in enhancing the metal's purity. The compound assists in the removal of undesirable elements, resulting in magnesium alloys with improved strength, corrosion resistance, and overall performance. These alloys find applications in lightweight automotive components and advanced aerospace technologies.
Eco-Friendly Edge:
Beyond its refining prowess, potassium fluoroborate brings an eco-friendly dimension to the process. Compared to some traditional refining agents, potassium fluoroborate offers a more sustainable option, minimizing environmental impact. As industries increasingly focus on green practices, the use of this compound aligns with the global push for cleaner, greener technologies.
Innovations in Alloy Development:
Potassium fluoroborate doesn't stop at refining; it also contributes to the development of innovative alloys. By fine-tuning the composition of aluminum and magnesium alloys, manufacturers can achieve desired properties, such as increased strength, durability, and heat resistance. This versatility opens doors to a myriad of applications, from high-performance automobile parts to lightweight structural materials.
Challenges and Future Prospects:
While potassium fluoroborate has proven to be a valuable asset in metal refining, ongoing research seeks to address challenges and further improve the process. Scientists and engineers are exploring ways to enhance efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and minimize waste, ushering in a new era of sustainable metal production.
Potassium fluoroborate, often overlooked in the grand scheme of chemical compounds, emerges as a hero in the refining of aluminum and magnesium. Its ability to selectively remove impurities, improve electrolysis efficiency, and contribute to eco-friendly practices positions it as a catalyst for excellence in the world of metallurgy. As industries continue to push the boundaries of innovation, potassium fluoroborate stands ready to play a crucial role in shaping the future of high-quality, sustainable metal production.
- Fluoride Salt
- Ammonium Fluoride
- Sodium Fluoride
- Potassium Fluoride
- Sodium Hydrogenfluoride
- Potassium Bifluoride
- Magnesium Fluoride
- Aluminium Fluoride
- Barium Fluoride
- Lithium Fluoride
- Strontium Fluoride
- Nickel Fluoride
- Zinc Fluoride




