The Production and Application of Hydrofluoric Acid as a Refrigerant in Refrigerators and Cooling Systems
Hydrofluoric acid (HF) plays a crucial role in the realm of refrigeration technology, serving as a fundamental component in the creation of refrigerants utilized in appliances like refrigerators and cooling systems. This article delves into the intricate process of producing hydrofluoric acid and its subsequent application as a refrigerant, exploring the chemical reactions, environmental considerations, and the diverse applications across refrigeration devices.
1. Hydrofluoric Acid Production:
Hydrofluoric acid is commonly produced through the reaction between fluorspar (calcium fluoride, CaF2) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4). The chemical equation is as follows:
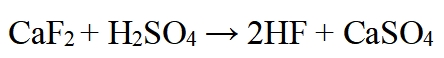
This reaction yields hydrofluoric acid and calcium sulfate. The produced hydrofluoric acid is then purified to meet the required standards for its various applications.
2. Hydrofluoric Acid as a Refrigerant:
Hydrofluoric acid undergoes further processing to be transformed into hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), a class of refrigerants commonly used in modern refrigeration systems. HFCs offer improved environmental performance compared to their predecessors, such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs), which are known for their ozone-depleting potential.
3. Chemical Reactions in Refrigeration:
The refrigeration cycle involves several key stages: compression, condensation, expansion, and evaporation. Hydrofluoric acid, in its refined form as an HFC, actively participates in these stages, facilitating the absorption and release of heat to achieve temperature control.
4. Environmental Considerations:
While hydrofluorocarbons have lower ozone-depleting potential than previous refrigerants, they are not entirely without environmental impact. Researchers are continually exploring alternative refrigerants with even lower global warming potential to mitigate the ecological footprint of refrigeration systems.
5. Applications in Refrigerators:
In household refrigerators, hydrofluoric acid-based refrigerants contribute to the efficient cooling of the interior space. The refrigerant circulates through a closed system, undergoing phase changes that absorb and release heat, maintaining the desired low temperature inside the refrigerator.
6. Industrial Cooling Systems:
Hydrofluoric acid-based refrigerants find extensive use in industrial cooling systems, such as large-scale refrigeration units. These systems play a critical role in various industrial processes, ensuring optimal operating temperatures for machinery and production facilities.
7. Air Conditioning Systems:
Air conditioning units, both residential and commercial, rely on hydrofluoric acid-based refrigerants to cool and dehumidify the air. The efficiency of these systems is greatly enhanced by the unique properties of hydrofluoric acid as a refrigerant.

Hydrofluoric acid's journey from production to application as a refrigerant in appliances represents a critical nexus of chemistry, technology, and environmental consciousness. Its role in the refrigeration cycle showcases the adaptability and efficiency of hydrofluoric acid-based refrigerants in meeting the cooling needs of diverse applications, from household refrigerators to large-scale industrial cooling systems. As the quest for sustainable practices persists, the evolution of refrigerants will likely continue, ushering in a new era of environmentally friendly cooling solutions.
- Fluoride Salt
- Ammonium Fluoride
- Sodium Fluoride
- Potassium Fluoride
- Sodium Hydrogenfluoride
- Potassium Bifluoride
- Magnesium Fluoride
- Aluminium Fluoride
- Barium Fluoride
- Lithium Fluoride
- Strontium Fluoride
- Nickel Fluoride
- Zinc Fluoride




