The Remarkable Role of Fluoroboric Acid in Oil Fields
In the vast world of oil exploration and production, various chemicals and substances play crucial roles in maintaining and enhancing the productivity of oil wells. One such chemical is fluoroboric acid, often referred to as HBF4. While it might sound like a complex and mysterious compound, this article aims to shed light on the role of fluoroboric acid in the oil field, explaining its properties, applications, and benefits in a simple and accessible manner.
What Is Fluoroboric Acid?
Fluoroboric acid is a chemical compound composed of hydrogen (H), boron (B), and fluorine (F). Its chemical formula is HBF4. It's a colorless, corrosive liquid with a sharp, pungent odor. Don't let the chemical formula intimidate you; we'll explore its role in the oil field step by step.
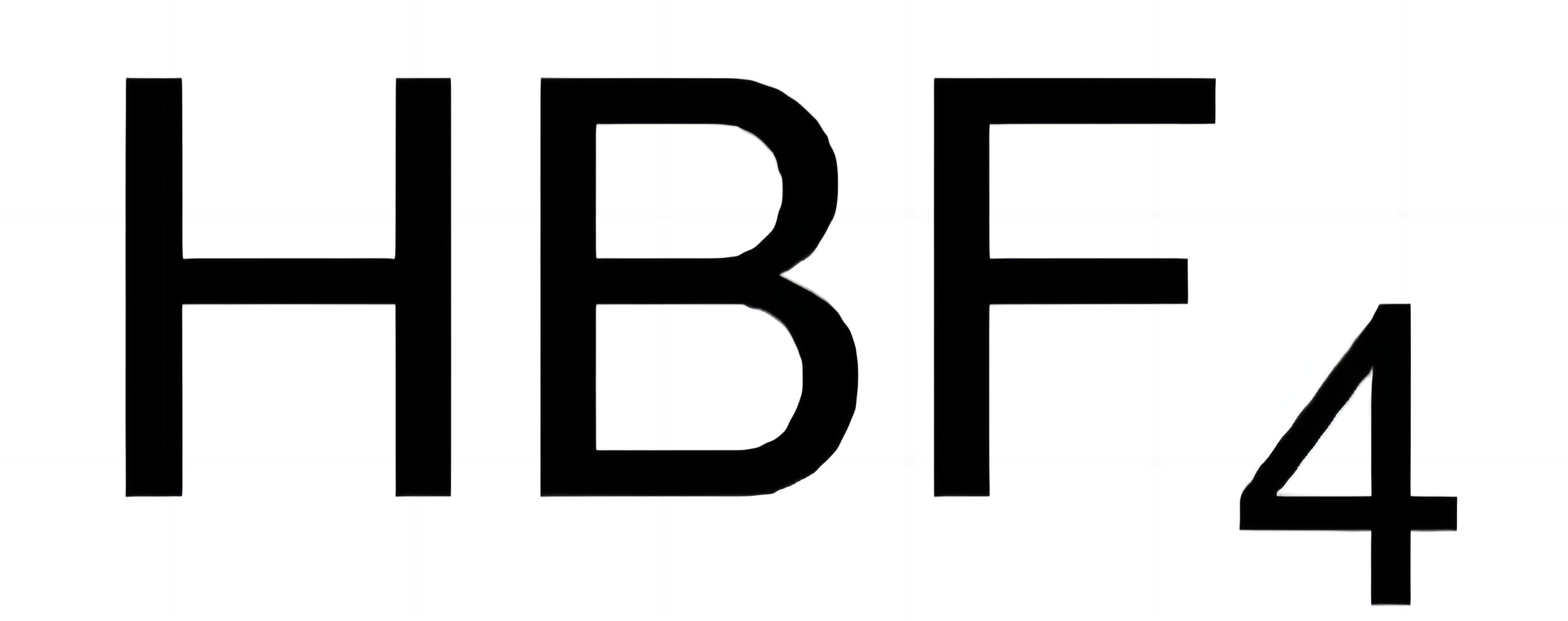
The Chemistry Behind Fluoroboric Acid
To understand how fluoroboric acid works in the oil field, let's delve into its chemistry. Fluoroboric acid is an example of a strong acid, which means it can easily donate hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water. This property makes it highly reactive. When it comes into contact with various minerals and substances found in oil wells, fascinating reactions occur.
1、Breaking Down Deposits
One of the primary applications of fluoroboric acid in oil fields is breaking down deposits. Over time, oil wells can become clogged with deposits such as carbonate minerals, sulfides, and silicates. These deposits reduce the well's productivity. Here's how fluoroboric acid helps:
● l When introduced into the well, fluoroboric acid reacts with these stubborn deposits, breaking them down into soluble components.
● As the deposits dissolve, they no longer obstruct the wellbore or reservoir pores, allowing oil to flow more freely.
● This process rejuvenates the well, improving its productivity and extending its lifespan.
2、Tackling Scale and Scale Prevention
Scale buildup is another common challenge in oil wells. Scale forms when minerals in the produced water precipitate and adhere to surfaces. Fluoroboric acid plays a vital role in tackling scale:
● By dissolving scale deposits, it prevents blockages in pipes, pumps, and equipment.
● Regular use of fluoroboric acid as a scale inhibitor helps maintain the efficiency of oil field operations.
3、Enhancing Production
In the oil industry, production rates are a critical factor. Fluoroboric acid contributes to enhanced production in several ways:
● Acting as an acidizing agent, it improves the flow properties of crude oil by reducing viscosity.
● The acid reacts with reservoir rock, increasing permeability and facilitating the movement of oil to the wellbore.
● This results in increased production rates and improved well performance.

Safety and Environmental Considerations
While fluoroboric acid is a powerful tool, it must be handled with care. Its corrosive nature can pose risks to both equipment and the environment. Thus, strict safety protocols must be followed when using fluoroboric acid in oilfields. Protective measures and trained personnel are essential to ensure safety and minimize environmental impacts.
Fluoroboric acid, with its remarkable chemical properties, plays a vital role in the oil and gas industry. From dissolving deposits to combating scale and enhancing production rates, it proves its worth in various applications across the oilfield. However, its power must be harnessed responsibly, with safety and environmental protection at the forefront.
In conclusion, fluoroboric acid is a valuable asset in the toolbox of oilfield operators, helping to maintain well integrity, improve productivity, and ensure the efficient flow of hydrocarbons from reservoir to production facilities. As the oil and gas industry continues to evolve, the role of chemicals like fluoroboric acid remains essential in meeting energy demands around the world.
- Fluoride Salt
- Ammonium Fluoride
- Sodium Fluoride
- Potassium Fluoride
- Sodium Hydrogenfluoride
- Potassium Bifluoride
- Magnesium Fluoride
- Aluminium Fluoride
- Barium Fluoride
- Lithium Fluoride
- Strontium Fluoride
- Nickel Fluoride
- Zinc Fluoride




