The Utilization of Potassium Fluotitanate in the Production of High-Performance Electronic Materials and Devices
Potassium fluotitanate (K₂TiF₆) is a versatile inorganic compound with significant industrial applications, particularly in the field of electronic materials and components. This article investigates the diverse uses of K₂TiF₆ in the synthesis of advanced electronic materials, focusing on its role in producing high-purity titanium compounds, specialized ceramics, and other crucial materials for electronic devices. The synthesis methods, chemical reactions, and properties of the resulting materials are discussed to highlight K₂TiF₆'s contribution to technological advancements in electronics.

In the rapidly evolving landscape of electronic technology, the demand for high-performance materials is ever-increasing. Potassium fluotitanate (K₂TiF₆) has emerged as a critical compound in meeting these demands due to its unique properties and applications. This compound is primarily used as a source of high-purity titanium, which is essential in the production of various electronic materials. This article delves into the industrial applications of K₂TiF₆, exploring its role in synthesizing materials that are foundational to modern electronic devices.
High-Purity Titanium and Its Derivatives
Titanium Purification and Alloy Production
The production of high-purity titanium is a cornerstone of advanced electronic materials. K₂TiF₆ plays a vital role in the purification process of titanium. The compound reacts with titanium ores to form soluble complexes, which can be reduced to yield pure titanium. This high-purity titanium is indispensable in manufacturing electronic components such as semiconductors, where impurities can significantly affect performance.
Titanium-Based Compounds
K₂TiF6 is also crucial in synthesizing various titanium-based compounds used in electronics. For instance, titanium potassium oxide (K₂TiO₃) crystals, produced using K2TiF6, are valued for their dielectric properties. These crystals are used in applications like capacitors and resonators, where high dielectric constants are required.
Advanced Ceramics for Electronics
Synthesis of Barium Titanate
Barium titanate (BaTiO₃) is a key material in the electronics industry, known for its high dielectric constant and ferroelectric properties. K₂TiF₆ serves as a titanium source in the production of BaTiO₃. The synthesis process involves reacting K₂TiF₆ with barium salts, resulting in the formation of BaTiO₃:
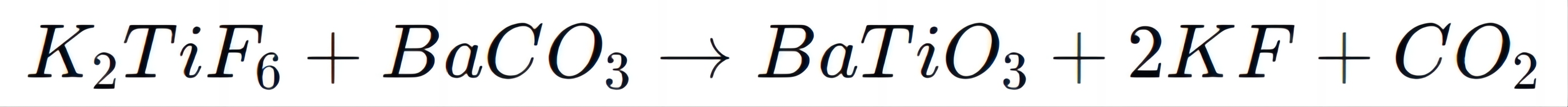
The ability to control the purity and particle size of BaTiO₃ is crucial for its performance in applications such as capacitors and transducers.
Production of Strontium Titanate
Strontium titanate (SrTiO₃) is another significant material synthesized using K₂TiF₆. SrTiO₃ is widely used in high-frequency electronics and photonic devices due to its excellent optical properties. The synthesis involves a reaction between K₂TiF₆ and strontium salts:
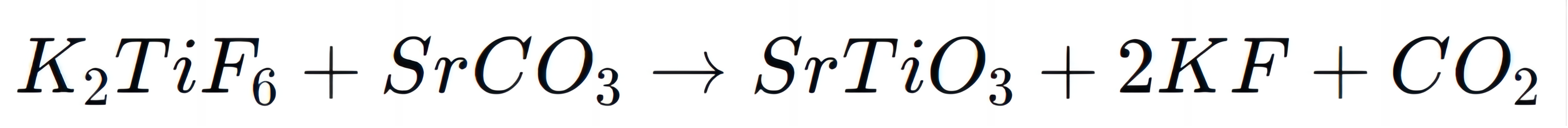
SrTiO₃ crystals produced through this method are integral in applications that require materials with high refractive indices and dielectric constants.
Titanium Fluoride in Coatings and Thin Films
Titanium fluoride (TiF₄) is an important compound derived from K₂TiF₆, used extensively in coatings and thin films. The production of TiF₄ involves reacting K₂TiF₆ with hydrogen fluoride (HF):
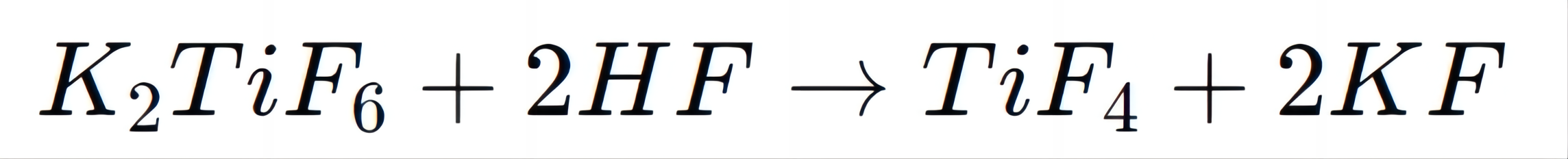
TiF₄ is used in chemical vapor deposition (CVD) processes to create titanium dioxide (TiO₂) thin films, which are essential in semiconductor devices, photovoltaic cells, and protective coatings due to their excellent optical and electronic properties.
Applications in Electronic Devices
Capacitors and Dielectrics
The high dielectric constants of materials like BaTiO₃ and SrTiO₃ make them ideal for use in capacitors. Multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs), which are fundamental components in modern electronics, benefit significantly from these materials. K₂TiF₆ - derived compounds ensure the high performance and reliability required in these capacitors.

Piezoelectric Components
Piezoelectric materials, such as barium titanate and potassium titanate, are critical in the production of sensors, actuators, and ultrasonic transducers. These materials convert mechanical energy into electrical energy and vice versa, making them indispensable in various applications, including medical imaging and industrial sensing.
Photonic Devices
Strontium titanate and other titanium-based compounds synthesized from K₂TiF₆ are essential in photonic devices. These materials' high refractive indices and optical clarity make them suitable for LEDs, laser diodes, and other devices that manipulate light. Their use enhances the efficiency and performance of these photonic components.
Potassium fluotitanate is a pivotal compound in the industrial production of high-performance electronic materials and devices. Its role in synthesizing high-purity titanium, advanced ceramics, and titanium fluoride underscores its versatility and importance. By enabling the creation of materials with superior dielectric, optical, and electronic properties, K₂TiF₆ drives innovation and technological progress in the electronics industry. Continued research and development in the applications of K₂TiF₆ will further enhance its impact, fostering the advancement of next-generation electronic devices.
References
[Relevant scientific journal articles]
[Industry reports and technical papers]
[Books on inorganic chemistry and material science]




