Understanding the Applications of Zinc Fluorosilicate in Protective Glass
Protective glass plays a vital role in safeguarding various applications, ranging from nuclear facilities to medical equipment and industrial settings. Among the materials used to enhance the protective qualities of glass, zinc fluorosilicate stands out as an essential component. In this informative article, we will explore the principles, methods, and extensive scope of zinc fluorosilicate applications in protective glass.
Principles of Zinc Fluorosilicate Application
Zinc fluorosilicate, a unique compound, is a versatile material known for its exceptional protective properties. When applied to glass surfaces, it serves several fundamental principles:
1、Radiation Shielding: One of the primary applications of zinc fluorosilicate in protective glass is its ability to shield against harmful radiation. This compound attenuates ionizing radiation, reducing its transmission through the glass, and safeguarding personnel from radiation hazards. This principle is crucial in nuclear facilities, medical radiology rooms, and research laboratories where radiation protection is paramount.
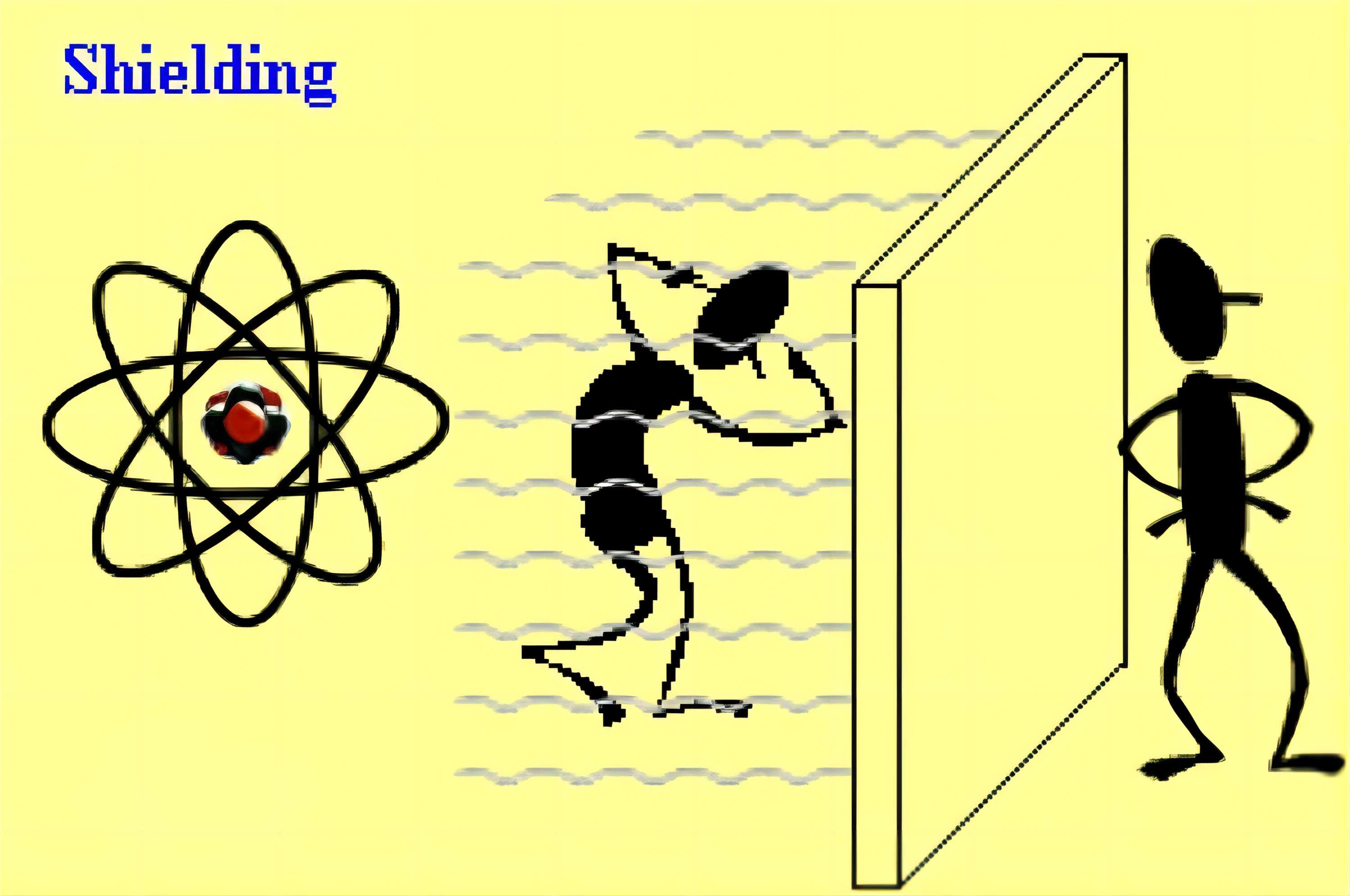
2、Corrosion Resistance: Zinc fluorosilicate coatings provide excellent corrosion resistance, preventing aggressive chemicals from damaging the glass surface. This property is especially valuable in chemical and pharmaceutical industries, where glass equipment is exposed to corrosive substances.
3、Abrasion Resistance: The application of zinc fluorosilicate enhances the glass's resistance to wear and abrasion. This makes it suitable for applications in industries like automotive and military, where the glass may be subjected to scratches and abrasive forces.
4、Optical Transparency: Zinc fluorosilicate coatings are transparent, ensuring that the glass remains optically clear. This transparency is essential for maintaining visual clarity and light transmission, making the glass suitable for various optical applications.
Methods of Applying Zinc Fluorosilicate
Applying zinc fluorosilicate to protective glass is a specialized process that requires precision and expertise. Several methods are employed to ensure a uniform and effective application:
▲ Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): Chemical vapor deposition is a common technique for depositing zinc fluorosilicate coatings onto glass surfaces. In this method, the glass is exposed to chemical precursors in a controlled environment. These precursors react to form a thin, uniform layer of zinc fluorosilicate on the glass. CVD is suitable for large-scale production and ensures consistent coating thickness.
▲ Sputtering: Sputtering is another method that involves bombarding a zinc fluorosilicate target with high-energy ions. The resulting ejected atoms or molecules are then deposited onto the glass substrate, creating a thin protective layer. This technique offers precise control over the coating's thickness and is well-suited for small-scale or custom applications.
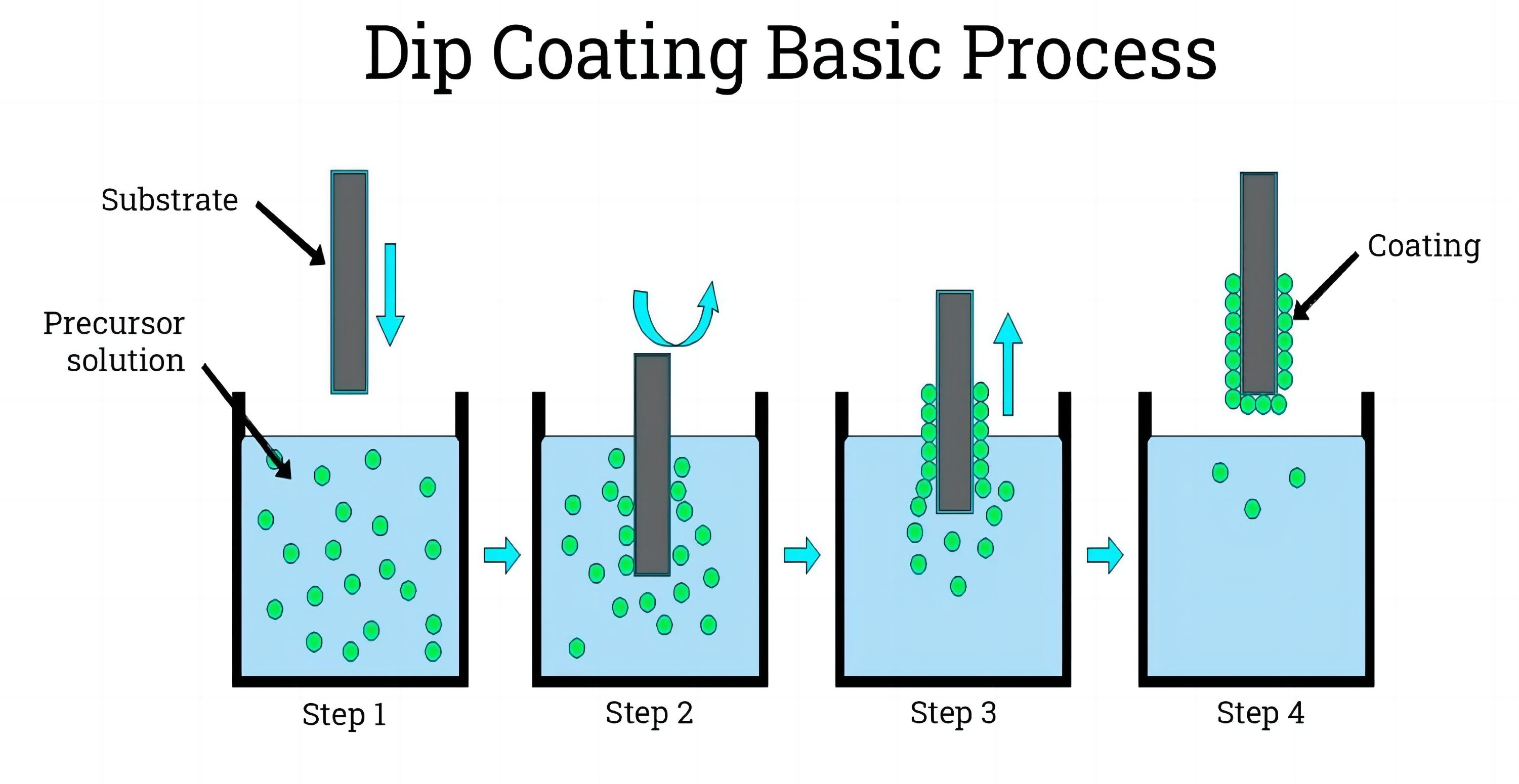
▲ Dip Coating: Dip coating involves immersing the glass into a solution containing zinc fluorosilicate, followed by drying and curing to form the protective layer. While this method is less precise in terms of coating thickness, it is cost-effective and suitable for smaller-scale projects.
▲ Spray Coating: Spray coating is the process of spraying a zinc fluorosilicate solution onto the glass surface using specialized equipment. This method is versatile and can be adapted to various glass shapes and sizes, making it suitable for a range of applications.
Scope of Zinc Fluorosilicate Applications
The use of zinc fluorosilicate in protective glass extends to a wide array of industries and applications, ensuring safety, durability, and clarity. Some of the key application areas include:
1、Nuclear Industry: Protective glass with zinc fluorosilicate coatings is integral to nuclear facilities, including power plants and research reactors. It provides vital radiation shielding to protect workers and prevent radiation leakage.
2、Medical Radiology: Radiology rooms in hospitals and clinics utilize zinc fluorosilicate-coated glass to protect medical professionals and patients from harmful X-rays and gamma rays.
3、Chemical and Pharmaceutical Industry: Glass equipment used in chemical synthesis and pharmaceutical manufacturing benefits from zinc fluorosilicate coatings, which prevent corrosion and extend the lifespan of the glassware.
4、Aerospace and Defense: Protective glass for military vehicles, aircraft, and military optics often incorporates zinc fluorosilicate coatings for abrasion resistance and improved optical clarity.
5、Laboratory Equipment: Laboratories that handle hazardous chemicals or conduct experiments involving ionizing radiation utilize protective glass with zinc fluorosilicate coatings for safety and durability.
6、Security and Surveillance: Protective glass used in security cameras and observation windows benefits from zinc fluorosilicate coatings to ensure long-term clarity and protection against environmental elements.

7、Optical Instruments: Telescopes, binoculars, and other optical instruments benefit from zinc fluorosilicate-coated glass to enhance optical performance and extend the life of the equipment.
In summary, zinc fluorosilicate plays a crucial role in enhancing the protective qualities of glass in a variety of applications. Its ability to shield against radiation, resist corrosion, and increase abrasion resistance makes it an invaluable component in protective glass solutions. The methods of application, such as CVD, sputtering, dip coating, and spray coating, ensure that zinc fluorosilicate can be tailored to meet the specific needs of different industries. From nuclear facilities to medical radiology rooms, and from laboratories to military vehicles, the scope of zinc fluorosilicate applications in protective glass is both broad and vital to ensuring safety, durability, and clarity in a wide range of settings.




