Fluorosilicic Acid as A Versatile Corrosion Inhibitor
Fluorosilicic acid, a compound commonly found in various industrial applications, serves as an effective corrosion inhibitor. Its remarkable properties make it a go-to solution in combating corrosion across diverse sectors, ranging from metal surfaces to concrete structures. This article delves into the science behind its corrosion-resistant capabilities and explores its specific applications in corrosion prevention.
Fluorosilicic acid, with the chemical formula H2SiF6, owes its corrosion inhibition capabilities to its reaction with metal surfaces. When applied to a metal substrate, such as iron or steel, it undergoes hydrolysis in the presence of water:
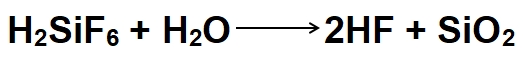
This reaction generates hydrofluoric acid (HF) and silica (SiO2). The HF produced acts as a proton donor, forming a protective layer of metal fluoride on the metal surface:
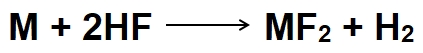
Here, M represents the metal substrate. The metal fluoride layer serves as a barrier, preventing further corrosion by shielding the underlying metal from corrosive agents.
Applications in Various Industries:
1、Metalworking Industry:
In the metalworking industry, fluorosilicic acid finds widespread use as a corrosion inhibitor for ferrous and non-ferrous metals. When applied to metal surfaces, it undergoes hydrolysis to produce hydrofluoric acid (HF), which reacts with the metal substrate to form a protective metal fluoride layer. This layer acts as a barrier against corrosive agents, extending the lifespan of components such as pipelines, storage tanks, and machinery.
2、Construction Sector:
In construction, fluorosilicic acid serves as a corrosion inhibitor and concrete sealer. When added to concrete mixtures, it reacts with calcium ions present in the cement matrix, generating calcium fluoride (CaF2) and silica gel. This reaction results in the formation of a dense, impermeable layer on the concrete surface, enhancing its resistance to chemical attack and reinforcing its structural integrity. Fluorosilicic acid-treated concrete structures exhibit prolonged durability, particularly in environments prone to corrosion.
3、Glass Manufacturing and Treatment:
Fluorosilicic acid plays a crucial role in glass manufacturing and treatment processes as a corrosion inhibitor. When applied to glass surfaces, it reacts with metal oxides, such as those of aluminum and magnesium, to form metal fluorides and silica gel. This reaction creates a durable, hydrophobic coating on the glass, preventing corrosion and enhancing its longevity, especially in applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
4、Timber Industry:
In the timber industry, fluorosilicic acid is utilized as a wood preservative and corrosion inhibitor. When applied to wooden surfaces, it forms stable metal fluoride complexes through reactions with cellulose and lignin components. These complexes penetrate deep into the wood, providing long-lasting protection against fungal decay and insect infestation. Fluorosilicic acid-treated wood products exhibit enhanced durability and resistance to environmental degradation, thereby extending their lifespan.

Fluorosilicic acid, with its remarkable corrosion inhibition properties, plays a vital role in various industries. Through chemical reactions that result in the formation of protective coatings, it effectively safeguards metal, concrete, glass, and wood surfaces from corrosion and degradation. As technology continues to advance, the applications of fluorosilicic acid as a corrosion inhibitor are expected to expand, contributing to the longevity and sustainability of diverse materials and structures.
- Fluoride Salt
- Ammonium Fluoride
- Sodium Fluoride
- Potassium Fluoride
- Sodium Hydrogenfluoride
- Potassium Bifluoride
- Magnesium Fluoride
- Aluminium Fluoride
- Barium Fluoride
- Lithium Fluoride
- Strontium Fluoride
- Nickel Fluoride
- Zinc Fluoride




