How Can Ammonium Hexafluorozirconate be Used in Electroplating
Electroplating is a crucial process in various industries, used to enhance the properties of metal surfaces. Ammonium hexafluorozirconate (NH4)2ZrF6 is a chemical compound that plays a significant role in this process. This article explores the application of ammonium hexafluorozirconate in electroplating, detailing its functions and benefits in achieving high-quality metal finishes.
Understanding Electroplating
Electroplating involves deposi
ting a thin layer of metal onto a substrate through an electrochemical process. This technique is employed to improve corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and aesthetic appeal. For successful electroplating, meticulous surface preparation is crucial. Ammonium hexafluorozirconate plays a vital role in this preparatory phase, ensuring that the substrate surface is adequately cleaned and activated.
Importance of Surface Preparation
Before delving into the specific applications of ammonium hexafluorozirconate, it is essential to understand the importance of surface preparation in electroplating. A clean, well-prepared surface ensures that the electroplated metal layer adheres properly and uniformly. Any contaminants or oxides on the substrate can lead to poor adhesion, resulting in defects and reduced durability of the electroplated layer.
Applications of Ammonium Hexafluorozirconate
1. Cleaning Agent
Ammonium hexafluorozirconate is highly effective as a cleaning agent. It removes organic contaminants such as oils and greases, as well as inorganic impurities like oxides and scales. This thorough cleaning process is essential for creating a pristine surface that promotes strong adhesion of the electroplated metal.
2. Surface Activation
In addition to cleaning, ammonium hexafluorozirconate serves as an activator for the substrate surface. Surface activation involves etching the metal, creating a microscopically rough surface that enhances the mechanical bonding of the electroplated layer. The roughened surface provides more nucleation sites for the deposited metal, resulting in a more uniform and defect-free layer.
3. Oxide Layer Removal
Metal surfaces often have a thin oxide layer that can hinder the adhesion of the electroplated metal. Ammonium hexafluorozirconate effectively removes these oxide layers. The compound dissociates in solution, releasing fluoride ions (F-) that react with the metal oxides, converting them into soluble complexes that are easily washed away. This process exposes a fresh, clean metal surface ideal for electroplating.
4. Improving Adhesion
The primary benefit of using ammonium hexafluorozirconate in surface preparation is the significant improvement in adhesion of the electroplated layer. The combination of cleaning, oxide removal, and surface activation ensures that the electroplated metal adheres strongly to the substrate. This enhanced adhesion is critical for the durability and performance of the electroplated component.
Step-by-Step Application in Electroplating
Step 1: Initial Cleaning
The first step in the electroplating process is to immerse the substrate in a cleaning solution containing ammonium hexafluorozirconate. This solution may also include other cleaning agents such as surfactants to help remove organic contaminants. The substrate is thoroughly cleaned to ensure that all surface impurities are eliminated.
Step 2: Rinsing
After cleaning, the substrate is rinsed with deionized water to remove any residual cleaning solution and loosened contaminants. Proper rinsing is essential to prevent any residues from interfering with subsequent steps.
Step 3: Surface Activation
The cleaned substrate is then treated in an activation bath containing ammonium hexafluorozirconate. This bath typically operates at specific concentrations and temperatures optimized for the substrate material. During this step, the surface is etched and activated, creating a roughened texture that promotes strong adhesion of the electroplated metal.
Step 4: Oxide Layer Removal
For substrates with significant oxide layers, an additional step of oxide removal may be performed using a more concentrated solution of ammonium hexafluorozirconate. This ensures that any remaining oxides are thoroughly dissolved, exposing a clean metal surface.
Step 5: Final Rinsing
Following activation and oxide removal, the substrate is again rinsed with deionized water to remove any residual chemicals and by-products of the etching process. This step ensures that the substrate is fully prepared for electroplating.
Step 6: Electroplating
The prepared substrate is now ready for the electroplating process. It is immersed in an electroplating bath containing the metal to be deposited. The electrochemical reaction deposits a thin layer of metal onto the substrate. The quality of the electroplated layer is significantly enhanced by the thorough preparation with ammonium hexafluorozirconate, resulting in a uniform, adherent, and defect-free finish.
Chemical Reactions Involved
The effectiveness of ammonium hexafluorozirconate in surface preparation can be attributed to several key chemical reactions:
1、Dissociation in Solution:
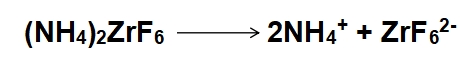
2、Oxide Removal:

where MxOy represents the metal oxides and MFy are the soluble complexes formed.
3、Surface Etching:
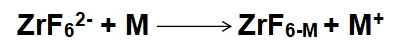
where M is the metal substrate being etched.
These reactions highlight the compound's role in breaking down contaminants and oxides, facilitating a clean and activated surface ready for electroplating.
Benefits of Using Ammonium Hexafluorozirconate
Enhanced Adhesion
The primary advantage of using ammonium hexafluorozirconate is the improved adhesion of the electroplated metal. By creating a clean, activated surface, the electroplated layer bonds more strongly to the substrate, resulting in a more durable and reliable finish.
Uniform Coating
The activation process ensures a uniform surface texture, promoting even deposition of the electroplated metal. This uniformity is crucial for applications where consistent coating thickness is required.
Reduced Defects
By thoroughly cleaning and activating the substrate, the use of ammonium hexafluorozirconate reduces the occurrence of defects such as pits, voids, and poor adhesion areas in the electroplated layer. This leads to higher quality and performance of the electroplated components.
Improved Corrosion Resistance
A well-adhered and uniform electroplated layer provides better protection against corrosion. The initial cleaning and activation steps help ensure that the electroplated metal covers the substrate completely, minimizing exposure to corrosive environments.
Ammonium hexafluorozirconate (NH4)2ZrF6 plays a critical role in the electroplating industry, particularly in the pre-treatment stages. Its effectiveness in cleaning, activating, and removing oxide layers from metal substrates ensures that the electroplated metal adheres strongly and uniformly. The result is a high-quality, durable electroplated finish that meets the demanding requirements of various industrial applications. Understanding and optimizing the use of ammonium hexafluorozirconate in electroplating processes can lead to significant improvements in the performance and longevity of electroplated products.




