Why Ammonium Fluoride is Key for Aluminum Surface Passivation
Aluminum is a versatile metal known for its strength, lightweight nature, and natural corrosion resistance, which makes it ideal for industries like aerospace, automotive, and electronics. However, despite its advantages, aluminum still requires surface treatments to maximize its performance in demanding environments. One such surface treatment is passivation, a process that enhances aluminum’s resistance to corrosion and prepares it for coatings or further processing.
Among the various chemicals used in the aluminum passivation process, ammonium fluoride (NH4F) plays a crucial role. Ammonium fluoride is especially valuable due to its unique chemical properties that enable it to clean, etch, and prepare aluminum surfaces effectively. This article explores why ammonium fluoride is essential in aluminum passivation, focusing on the principles, chemical mechanisms, and detailed process by which it optimizes aluminum surfaces for durability and further processing.

Understanding Aluminum Surface Passivation
Passivation is a surface treatment process that enhances the corrosion resistance of metals by forming a stable, protective oxide layer. While aluminum naturally forms a thin oxide layer when exposed to air, this layer can sometimes be irregular or contaminated, affecting its protective qualities and hindering adhesion for subsequent coatings or treatments. Passivation using ammonium fluoride helps modify this oxide layer to make it more uniform, stable, and resistant to further corrosion.
The aluminum passivation process typically includes several stages: initial cleaning, etching, and a final treatment that strengthens the surface. Ammonium fluoride is particularly useful in the etching and cleaning stages, where it helps remove impurities and prepares the aluminum for passivation.
Why Ammonium Fluoride Works in Aluminum Passivation
The effectiveness of ammonium fluoride in aluminum passivation lies in its unique chemistry, which enables it to interact with aluminum oxide. When aluminum is exposed to ammonium fluoride, the compound breaks down into ammonium ions (NH₄⁺) and fluoride ions (F⁻), which play distinct roles in surface preparation. The primary reasons ammonium fluoride is effective in aluminum passivation include:
1、Removal of Aluminum Oxide Layers:
Aluminum naturally forms an oxide layer (Al2O3) on its surface. While this oxide layer provides some corrosion resistance, it can also interfere with adhesion when additional coatings or treatments are applied. The fluoride ions from ammonium fluoride react with aluminum oxide, dissolving it and exposing fresh aluminum underneath. This reaction is critical for creating a uniform and receptive surface.
2、Surface Etching for Improved Adhesion:
Beyond removing aluminum oxide, ammonium fluoride also helps roughen the aluminum surface. The etching process increases the surface area and creates microstructures that improve the adhesion of coatings or anodizing layers, which is essential for durability in industrial applications.
3、Enhanced Cleanliness:
Ammonium fluoride effectively removes organic residues, oils, and other contaminants from the aluminum surface. This cleaning action is crucial because contaminants can inhibit passivation and weaken the bond between the aluminum and any applied coatings or treatments.
The Chemical Mechanism of Ammonium Fluoride in Aluminum Oxide Removal
The effectiveness of ammonium fluoride lies in its chemical ability to break down the aluminum oxide layer. When ammonium fluoride (NH4F) is applied to an aluminum surface, it dissociates in solution into fluoride ions (F-) and ammonium ions (NH4+). The fluoride ions, being highly reactive, interact with the aluminum oxide layer (Al2O3) according to the following reaction:
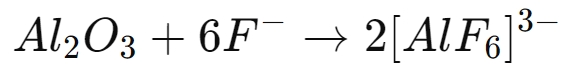
This reaction forms soluble aluminum-fluoride complexes, effectively dissolving the aluminum oxide layer and leaving a clean, exposed aluminum surface. The dissolution of the oxide layer prepares the surface for passivation by removing any irregularities and ensuring uniformity.
The fluoride ions are particularly efficient in targeting and dissolving aluminum oxide without significantly affecting the underlying aluminum, which allows for a controlled etching process. By dissolving the oxide layer, ammonium fluoride reveals a fresh aluminum surface that can bond effectively with additional treatments or coatings.
Detailed Process of Aluminum Passivation Using Ammonium Fluoride
The aluminum passivation process using ammonium fluoride typically involves several stages, each designed to maximize the metal’s durability and suitability for further treatments. The process generally follows these steps:
1、Initial Cleaning:
The aluminum surface is first cleaned to remove any oils, grease, or particulate contaminants. This may involve washing with an alkaline solution or degreasing agents to ensure that the surface is free from substances that could interfere with ammonium fluoride.
2、Application of Ammonium Fluoride:
The aluminum is then immersed in an aqueous solution containing ammonium fluoride, often mixed with other acids to create a controlled pH environment. During immersion, the ammonium fluoride breaks down into ammonium and fluoride ions, which initiate the etching and oxide removal process. The concentration of ammonium fluoride and the immersion time are carefully controlled to achieve the desired level of surface preparation without excessive material loss.
3、Oxide Removal and Surface Etching:
During the ammonium fluoride treatment, fluoride ions react with the aluminum oxide layer, dissolving it and leaving behind a clean aluminum surface. The etching process simultaneously creates microscopic pits and roughness on the aluminum surface, improving its adhesion properties. This roughened surface is especially valuable for industrial applications that require strong, durable bonds between the aluminum and protective coatings.
4、Rinsing:
After etching, the aluminum surface is thoroughly rinsed with deionized water to remove any residual ammonium fluoride and reaction by-products. This step ensures that no residual chemicals remain, which could affect the quality of the subsequent passivation layer or protective coating.
5、Passivation Treatment:
Once the surface has been etched and cleaned, the aluminum undergoes the actual passivation process. This may involve anodizing (an electrochemical process that thickens the oxide layer), chromate conversion, or applying another form of protective coating. The freshly prepared aluminum surface is highly receptive to these treatments, allowing for a more uniform and durable passivation layer.
6、Final Rinse and Drying:
After the passivation or coating treatment, the aluminum is rinsed again and dried. The final result is a passivated aluminum surface with enhanced corrosion resistance and improved adhesion for coatings or treatments, making it ideal for demanding industrial applications.
Applications of Passivated Aluminum in Industry
The use of ammonium fluoride in the aluminum passivation process is widely adopted across various industries that require high-performance and corrosion-resistant aluminum components. Some of the key industries and applications include:
1、Aerospace:
In aerospace, aluminum is widely used in the production of structural components due to its lightweight and high strength. Passivation helps to improve the durability of these components, ensuring they can withstand the extreme conditions experienced during flight. Ammonium fluoride is especially valuable in preparing aluminum surfaces for anodizing, which provides an additional protective layer against corrosion and wear.

2、Automotive:
In the automotive sector, aluminum is used in engines, body panels, and other components. By enhancing the corrosion resistance and paint adhesion of aluminum surfaces, passivation with ammonium fluoride contributes to the longevity of automotive components, especially in harsh environments like those with high humidity, salt, or pollutants.
3、Electronics:
In electronics, aluminum passivation is critical for parts used in devices like heat sinks, casings, and conductive materials. The passivation layer provides insulation and prevents corrosion in components exposed to varying environmental conditions. Ammonium fluoride ensures that the passivation layer is uniform and firmly adheres to the surface, improving the component’s reliability.
4、Marine:
Aluminum is commonly used in the marine industry due to its natural resistance to saltwater corrosion. Passivation further enhances this property, ensuring that aluminum components, such as hulls, fittings, and frames, last longer in the challenging marine environment. The use of ammonium fluoride is essential in preparing these surfaces to withstand saltwater exposure.
Ammonium fluoride plays an indispensable role in the passivation of aluminum by providing efficient oxide layer removal and surface etching. Its ability to chemically dissolve the natural oxide layer and prepare a roughened surface makes it ideal for applications where high-performance aluminum components are required. The unique properties of ammonium fluoride help maximize aluminum’s durability, corrosion resistance, and adhesion capabilities, making it a vital component in industries that rely on aluminum for strength and longevity.




