The Principle and Advantages of Using Hexafluorosilicic Acid as a Wet Etchant in the Electronics Industry
The rapid evolution of the electronics industry has necessitated the development of advanced chemical processes to meet the demand for smaller, more efficient, and highly integrated devices. Among these processes, wet etching stands out as a critical step in manufacturing semiconductor devices. One chemical gaining prominence in this field is hexafluorosilicic acid (H2SiF6), a highly effective etching agent. This article delves into the principles of using hexafluorosilicic acid as a wet etchant, how it works, and the advantages it offers compared to alternative chemicals.
1、Understanding Hexafluorosilicic Acid
Hexafluorosilicic acid, a byproduct of phosphate fertilizer production, is a colorless, corrosive liquid comprising silicon and fluorine atoms. It has the chemical formula H2SiF6 and is known for its strong acidic properties and high reactivity with silica-based compounds. In wet etching, this reactivity is utilized to selectively remove layers of silicon dioxide (SiO2) from semiconductor wafers.
Although traditionally used in water fluoridation and other industrial applications, hexafluorosilicic acid has recently gained traction in the electronics sector due to its chemical efficiency and unique properties.
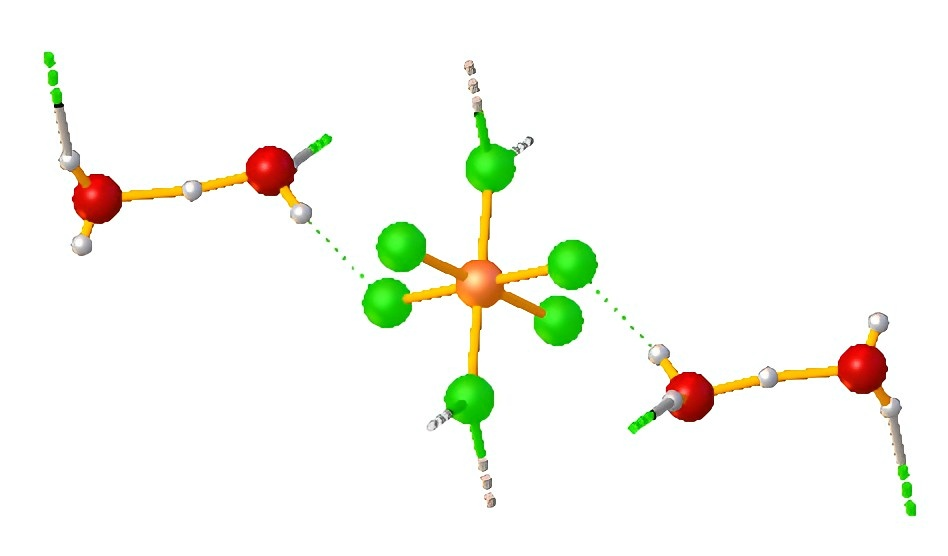
2、The Principle of Wet Etching with Hexafluorosilicic Acid
Wet etching involves immersing the material to be processed in a liquid chemical solution that selectively reacts with and dissolves targeted layers. For semiconductor manufacturing, silicon dioxide (SiO2) is a common material that requires precise etching to create pathways, insulating layers, and patterns essential for microelectronics.
a、Chemical Reaction Mechanism
When hexafluorosilicic acid is used as an etchant, it reacts with silicon dioxide through the following process:
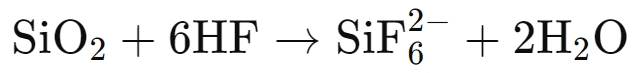
This reaction is highly efficient because:
⑴ High Selectivity: Hexafluorosilicic acid specifically targets silicon dioxide without significantly affecting the underlying silicon or other materials.
⑵ Controlled Reaction Rate: The reaction proceeds at a manageable rate, ensuring precision in material removal.
b、Process Flow
① Solution Preparation: Hexafluorosilicic acid is typically diluted with water and combined with hydrofluoric acid (HF) to enhance etching performance. The concentration of the acid determines the etching speed and selectivity.
② Immersion: The semiconductor wafer, coated with a layer of silicon dioxide, is immersed in the etching solution. The acid selectively reacts with the silicon dioxide, dissolving it into a water-soluble complex.
③ Rinsing and Drying: After etching, the wafer is thoroughly rinsed with deionized water to remove any residual acid. It is then dried, leaving a clean and precisely etched surface.
3、Advantages of Hexafluorosilicic Acid in Wet Etching
3.1、High Selectivity
One of the most significant advantages of hexafluorosilicic acid is its ability to selectively etch silicon dioxide while preserving the underlying silicon. This selectivity is crucial in semiconductor manufacturing, where precision is key to creating intricate circuits and patterns.
3.2. Uniform Etching
Hexafluorosilicic acid provides uniform etching across the wafer surface, making it ideal for processing large wafers used in modern electronics. This uniformity ensures consistent quality and reduces the risk of defects in the final product.
3.3. Lower Toxicity Compared to Alternatives
While hydrofluoric acid (HF) is a powerful etchant, its extreme toxicity and handling risks make it less desirable in some applications. Hexafluorosilicic acid, when diluted, poses fewer handling hazards, making it a safer alternative while maintaining high etching efficiency.
3.4. Cost-Effectiveness
As a byproduct of industrial processes, hexafluorosilicic acid is relatively inexpensive and widely available. Its cost-effectiveness makes it an attractive option for manufacturers seeking to optimize production costs without compromising quality.
3.5. Compatibility with Modern Techniques
Hexafluorosilicic acid integrates well with existing wet etching setups and can be used in conjunction with advanced photolithography and deposition techniques. This compatibility allows manufacturers to incorporate it into their processes with minimal disruption.

4、Comparison with Alternative Etching Agents
4.1. Hydrofluoric Acid (HF)
● Advantages: HF is a strong and fast etchant for silicon dioxide.
● Drawbacks: Its extreme toxicity and corrosive nature require stringent safety protocols, increasing operational complexity and costs.
4.2. Phosphoric Acid (H3PO4)
● Advantages: Phosphoric acid is less hazardous and can etch certain materials effectively.
● Drawbacks: It is not as effective in selectively etching silicon dioxide and is slower compared to hexafluorosilicic acid.
4.3. Dry Etching Techniques (e.g., Plasma Etching)
● Advantages: Dry etching offers precision at the nanoscale level, making it suitable for advanced applications.
● Drawbacks: It requires expensive equipment and higher operational costs, whereas hexafluorosilicic acid offers a simpler and more cost-effective solution for many applications.
5、Applications in the Electronics Industry
Hexafluorosilicic acid is utilized in several critical steps of semiconductor and electronics manufacturing:
5.1. Semiconductor Wafer Processing
It is widely used to etch silicon dioxide layers in semiconductor wafers, enabling the formation of pathways and insulating structures critical for microchip functionality.
5.2. Microelectromechanical Systems (MEMS)
MEMS devices, which include sensors, actuators, and microfluidic systems, require precise etching of silicon dioxide layers. Hexafluorosilicic acid ensures high-quality etching with minimal defects.
5.3. Solar Cell Production
In the photovoltaic industry, hexafluorosilicic acid is employed to clean and etch silicon wafers, preparing them for the deposition of energy-converting layers.
With the continuous advancement of semiconductor technology, the demand for efficient and cost-effective etching solutions is expected to grow. Research into improving the safety and environmental impact of hexafluorosilicic acid will further enhance its appeal in the electronics industry. Additionally, its compatibility with emerging nanotechnology applications positions it as a valuable tool for future innovations.
Hexafluorosilicic acid is an indispensable chemical in the electronics industry, particularly in the wet etching of silicon dioxide. Its high selectivity, cost-effectiveness, and compatibility with existing processes make it a preferred choice for semiconductor and microelectronics manufacturers. While challenges remain, the benefits of this versatile acid far outweigh its limitations, ensuring its continued relevance in the ever-evolving world of electronics manufacturing.




